diabetes2023影响因子_diabetes
1.什么是糖尿病
2.各种疾病名称以及其英文翻译(尽量多说)
3.糖尿病分为哪几型
4.diabetes mellitus这个单词的由来

type2 diabetes
翻译:糖尿病 多尿症 中消
权威例句
1.My doctor wants me to be tested for diabetes.
我的医生要我去做个检查,看是否患有糖尿病。
2.People with high blood pressure are especially vulnerable to diabetes.
有高血压的人尤其易患糖尿病。
3.He suffered from diabetes and gastric ulcers.
他患有糖尿病和胃溃疡。
什么是糖尿病
1. What is diabetes? Diabetes is a common endocrine diseases, Because the body is insulin absolute or relative lack of glucose and glucose concentrations increased, then a large number of sugar from the urine discharge, and there is more drinking, overeating, weight loss, dizziness, weakness and other symptoms. Further development has been the subject of serious systemic acute and chronic complications, threatening their health. With diabetes duration of the disease, the body's metabolism such as access to good control, which can lead to eye, kidney, nerve, such as cardiac and vascular tissues and organs of chronic complications, eventually happened blind, lower extremity damage, uremia, stroke or myocardial infarction, or even life-threatening. With the improvement of living standards, diabetes has become a common diseases, the incidence of diabetes is increasing year after year. Developed diabetes prevalence rate as high as 5% to 10%, China's average prevalence rate has reached 3% Some cities close to the prevalence in developed countries. 2. Diabetes type (1) Type 1 Diabetes type 1 diabetes, diabetic patients account for about 10% of the total. often occur in children and adolescents. It can happen at any age, even at the age of 80-90 also sick. Cause is insulin by the cell-mediated autoimmune destruction, not its own synthesis and secretion of insulin. (2) Type 2 Diabetes Type 2 diabetes, diabetes accounts for about 90% of the total, mostly in the age of onset after the age of 35, slow onset, and conceal some of the patients health checks or check for other diseases found. Type 2 diabetes patients, about 60% of the body weight of overweight or obese. Long-term excessive diet, high intake of calories, weight increase, as well as obesity, obesity after the lead to insulin resistance, elevated blood sugar, ketonemia no obvious trend. Most of the patients in control diet and oral hypoglycemic agents stable after treatment glucose; However, there are some patients in particular the non-obese patients need exogenous insulin to control blood sugar. Type 2 diabetes is obvious genetic, and the frequency of HLA antigen unrelated. (3) gestational diabetes in pregnant women found the original diabetes in pregnancy usually in the second trimester or later discovered diabetes, known as gestational diabetes mellitus. Have diabetes before pregnancy, gestational diabetes patients, diabetic patients as pregnancy. For early detection of diabetic pregnancy, usually in 24-28 weeks of pregnancy, oral administration of 50 grams of glucose, Sugar service half an hour after the blood test for glucose, glucose value if less than 7.8 cents mole / liter, may be excluded from gestational diabetes mellitus. If blood glucose greater than or equal to 7.8 mm mole / liter, it is possible pregnancy diabetes, need to take 100 grams of glucose tolerance test for diagnosis. (4) a special diabetes) cell function caused by genetic defects occurred adult-juvenile diabetes (MODY), Most age of onset before the age of 25, after the onset of at least five years or more do not need insulin treatment, is autosomal dominant inheritance. B) abnormal insulin gene caused diabetes. C) exocrine pancreatic diseases, such as pancreatitis, hemochromatosis, pancreatic resection caused by diabetes. D) endocrine diseases, such as acromegaly, Cushing's syndrome, pheochromocytoma, hyperthyroidism caused by diabetes. E) drug or chemical agents caused by diabetes. F) infection such as congenital rubella virus, cytomegalovirus infection caused by diabetes. G) a rare immune-mediated diabetes as insulin autoimmune syndrome. H) with diabetes other genetic syndrome. 3. The typical symptoms of diabetes (1) "a little more than 3" : multiple, polyuria, polyphagia, emaciated. (2) the occurrence of the typical symptoms of a fast, slow, light to heavy, these symptoms are different for every patient, a disease may be obvious, other prominent symptoms. Type 2 diabetes at the onset of symptoms is relatively slow, difficult to attract attention. Type 1 diabetes onset of symptoms often more apparent. 4. DIABETES genetic factors : a family of diabetics, their diabetes opportunities in the higher than normal. Obesity : middle age due to excessive food intake, lack of exercise, calories Poly growing body fat easy, easy with diabetes. Mental pressure : the chronic under pressure from the spirit of the people likely to cause endocrine disorders caused diabetes. Drugs : some drugs such as solid-type alcohol, oral contraceptives, can also cause diabetes. Pregnancy : pregnancy hormone changes, as one of the reasons diabetes. 5. What is normal blood glucose blood glucose is the presence of glucose, glucose said blood glucose concentration. In normal glucose fluctuations within a certain range, glucose oxidase rules intravenous plasma glucose level, fasting plasma glucose 3.4-6.2 mm in mole / liter; 2-hour blood sugar after meals is not more than 7.8 cents mole / liter.
各种疾病名称以及其英文翻译(尽量多说)
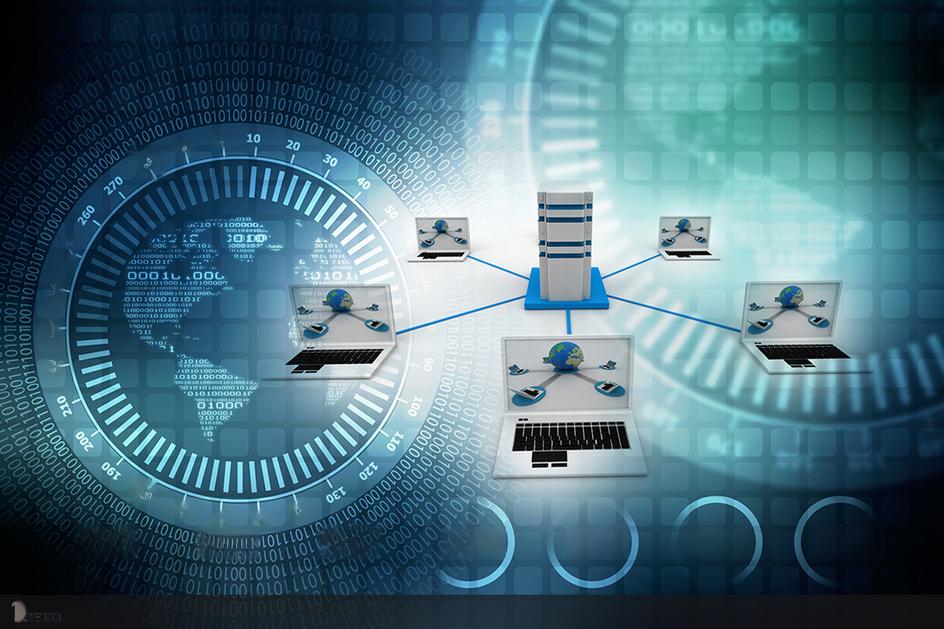
症状及分类 "糖尿病"是一种血液中的葡萄糖容易堆积过多的疾病。国外给它的别名叫"沉默的杀手"(Silent Killer),特别是"成人型糖尿病",四十岁以上的中年人染患率特别高,在日本,四十岁以上的人口中占10%,即十人当中就有一位"糖尿病"患者。一旦患上"糖尿病",将减少寿命十年之多,且可能发生的并发症遍及全身。 "糖尿病"本身亦给人带来非常的痛苦。它让人常常觉得口干想喝水,因多尿而半夜多次醒来。尽管已吃了不少食物仍觉饥饿感,体重减轻、嗜睡等等,总让人觉得周身哪处不对劲。等到能够感觉到某处的明显情况时,"糖尿病"的病情已发展到一定程度了。而可怕的并发症亦随之悄悄地在全身各处发展着。 所谓"糖尿病"并发症,可以上至头顶下至足底--忧虑、自律神经失调,神经障碍(手脚麻痹、知觉麻痹),脑血栓、脑梗阻、白内障、蛀牙、口腔炎、支气管炎、皮肤病、心肌梗塞、肺炎、肺结核、肝硬化、生育异常、流产、肾功能不健全、尿毒症、阳痿、女性下体发炎、膀胱炎、尿道炎、坏疽、足病变(水虫等)等等。 在这些并发症中,出现率最高的是视网膜症、肾病和神经障碍,被称为"糖尿病"的"三大并发症"。这三大并发症在"糖尿病"患生后二十年以内,有百分之八十的人一定会得患这些疾病。动脉硬化也包括在里面,这是因为血液中过剩的葡萄糖逐渐腐蚀全身器官及其组织的恶果。 一旦患上"糖尿病",人体的麻烦随其而至,因为免疫功能减弱,容易感染由感冒、肺炎、肺结核所引起的各种感染疾病,而且不易治愈。并可以选择性地破坏细胞,吞噬细胞。抗癌细胞的防御机能将会大大减弱,至使癌细胞活跃、聚集,导致引发癌病患。 引起并发症范围如此广泛的疾病,除了"糖尿病"之外几乎很少见。因为并发症的关系,故有人说一旦得了"糖尿病",寿命至少减去十年。 我国目前有超过9200万的糖尿病患,另外还有1亿5000人将成为患者,这样中国已经取代印度,成为全球糖尿病第一大国。 我国最早的医书《黄帝内经素问》及《灵枢》中就记载了“消渴症”这一病名。汉代名医张仲景《金匮要略》之消渴篇对“三多”症状亦有记载。唐朝初年,我国著名医家甄立言首先指出,消渴症患者的小便是甜的。 糖尿病(Diabetes)分1型糖尿病和2型糖尿病。在糖尿病患者中,2型糖尿病所占的比例约为95%。 1型糖尿病 其中1型糖尿病多发生于青少年,因胰岛素分泌缺乏,依赖外源性胰岛素补充以维持生命。 儿童糖尿病也是1型糖尿病常见发病对象,儿童1型糖尿病患者起病多数较急骤,几天内可突然表现明显多饮、多尿、每天饮水量和尿量可达几升、胃纳增加但体重下降。年幼者常见遗尿、消瘦引起家长注意。发病诱因常由于感染、饮食不当发病。婴幼儿患病特点常以遗尿的症状出现,多饮多尿容易被忽视,有的直到发生酮症酸中毒后才来就诊。 2型糖尿病 2型糖尿病多见于中、老年人,其胰岛素的分泌量并不低,甚至还偏高,临床表现为机体对胰岛素不够敏感,即胰岛素抵抗(Insulin Resistance,IR)。 胰岛素是人体胰腺B细胞分泌的身体内唯一的降血糖激素。 胰岛素抵抗是指体内周围组织对胰岛素的敏感性降低,外周组织如肌肉、脂肪对胰岛素促进葡萄糖的吸收、转化、利用发生了抵抗。 临床观察胰岛素抵抗普遍存在于2型糖尿病中,高达90%左右。 糖尿病可导致感染、心脏病变、脑血管病变、肾功能衰竭、双目失明、下肢坏疽等而成为致死致残的主要原因。 糖尿病高渗综合症是糖尿病的严重急性并发症,初始阶段可表现为多尿、多饮、倦怠乏力、反应迟钝等,随着机体失水量的增加病情急剧发展,出现嗜睡、定向障碍、癫痫样抽搐,偏瘫等类似脑卒中的症状,甚至昏迷。
糖尿病分为哪几型
1、catarrh [k?tɑ:(r)]卡他, 粘膜炎
2、chicken pox, varicella [?t?k?n?p?ks?'v?r?'sel?] 水痘
3、diabetes [?dabi:ti:z] 糖尿病
4、diphtheria [d?f?θ?ri?]白喉
5、eczema [?eks?m?]湿疹
6、epilepsy [?ep?lepsi]癫痫
7、erysipelas [?er?'s?p?l?s]丹毒
8、gangrene [?g?gri:n]坏疽
9、leukemia[lu:'ki:m?] 白血病
10、malaria[m?le?ri?] 疟疾
11、malnutrition [?m?lnju:?tr?n] 营养不良
12、measles [?mi:zlz]麻疹
14、poliomyelitis [?p?lma?'la?t?s]脊髓灰质炎
15、rabies[?re?bi:z] 狂犬病
16、rheumatism[?ru:m?t?z?m?]风湿病
17、rickets, rachitis?[?r?k?ts]佝偻病
18、scabies[?ske?bi:z] 疥疮
19、scarlet fever [?skɑ:l?t ?fi:v?]猩红热
20、sciatica [sat?k?]坐骨神经痛
21、 Renal stone[?ri:n?l st?un] 肾结石
扩展资料
常用医疗器械英文表达
1、Urine Analyzer 尿液分析仪
2、blood sugar analyzer 血糖分析仪
3、test strip 测试条
4、reagent 试剂
5、Semi-automaticBiochemical Analyzer 半自动生化分析仪
6、Automatic BloodCell Analyzer 全自动血细胞分析仪
7、Urine sedimentsanalyzer 尿沉渣
8、Bio-safety Cabinet 生物安全柜
9、Incubator 培养箱
10、High FrequencyElectrotome 高频电刀
11、shadowless lamp 无影灯
12、High speedrefrigerated centrifuge 高速冷冻离心机
13、hot air sterilizer 热空气消毒箱
14、microbiologicalincubator 微生物培养箱
15、Halogen light 卤素灯
16、disposable sterileinjector 一次性无菌注射针
17、injection set 注射器
18、disposable venousinfusion needle 一次性静脉输液针
diabetes mellitus这个单词的由来
糖尿病分为1型和2型。 1型糖尿病多见于青少年,在成年糖尿病患者中占10%—15%,它是由于体内产生胰岛素的β细胞被破坏,存留的胰岛β细胞极少,因此病人空腹和餐后4个点的胰岛素分泌极度低下,严重者C-肽也表现为空腹及餐后均低下。 2型糖尿病是由于胰岛素受体结合能力降低,病人对胰岛素产生抵抗,糖的利用发生障碍,以餐后血糖升高为其特点。胰岛素和C-肽释放,空腹基础值正常,高峰值延迟。1型糖尿病,80%—100%的B细胞死亡,胰岛素不能分泌或分泌下降,而2型糖尿病只是B细胞功能受损,而使分泌下降同时兼有抵抗。1型糖尿病包括1b型,最终都必须使用胰岛素控制血糖,排除做胰岛细胞移植手术后部分患者可以不用胰岛素。2型糖尿病一般用口服药物即可控制血糖,但也可以用胰岛素后改用口服药物。1型糖尿病血糖控制不良时,易出现微血管神经病变,如肾衰。2型糖尿病血糖控制不良时可引起各种并发症,如心脑血管病、高血压、糖尿病足冠心病等,其两者最大的区别就是B细胞死亡和B细胞受损功能下降的区别。但最终两者可以引发相同的临床状态,即都必须使用胰岛素控制血糖。
diabetes
[Date: 1500-1600; Language: Latin; Origin: Greek, from diabainein 'to pass through']
a serious disease in which there is too much sugar in your blood
来自希腊语“diabainein”,表示“超出”的意思。
参考:朗文当代词典
声明:本站所有文章资源内容,如无特殊说明或标注,均为采集网络资源。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系本站删除。